X-RAY TOPOGRAPHY (XRT) FOR ELECTRONICS
VISUALIZE DEFECTS IN MANY DIFFERENT CRYSTALLINE MATERIALS
- X-ray topography is an imaging technique based on Bragg diffraction. Diffraction topographic images record the intensity profile of a beam of X-rays diffracted by a crystal.
- A topography thus represents a two-dimensional spatial intensity mapping of reflected X-rays, i.e. the spatial fine structure of a Laue reflection.
- This intensity mapping reflects the distribution of scattering power inside the crystal; topographs, therefore, reveal the irregularities in a non-ideal crystal lattice.
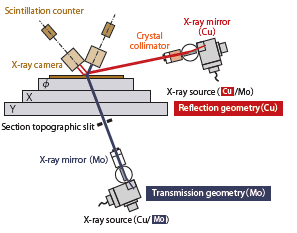
What is X-ray Topography?? X-ray diffraction topography is one variant of X-ray imaging, making use of diffraction contrast rather than absorption contrast which is usually used in radiography and computed tomography (CT). XRT is used for monitoring crystal quality and visualizing defects in many different crystalline materials. It has proved helpful e.g. when developing new crystal growth methods, for monitoring growth and the crystal quality achieved, and for iteratively optimizing growth conditions. In many cases, topography can be applied without preparing or otherwise damaging the sample; it is, therefore, one variant of non-destructive testing.
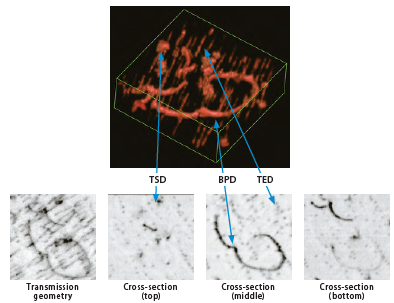
Below are a 3D image (1.2 mm × 1.2 mm × 0 .4 mm) showing the threading screw dislocation (TSD),
threading edge dislocation (TED), and basal plane dislocation (BPD), and their cross-section images.
The leftmost figure is a topographic image obtained by the standard transmission geometry.
SiC 3D dislocation image